That’s an excellent question, and the answer isn’t one-size-fits-all. The “best” side to sleep on depends on your specific health goals and conditions.
For most people, sleeping on your left side is considered the overall best position. However, each side has its own advantages and drawbacks.
Here’s a quick breakdown to help you decide what’s best for you.
The Champion: Left-Side Sleeping
Sleeping on your left side is most often recommended by doctors and sleep experts, particularly for:
-
Heart Health: For most people, the heart is on the left side of the body. Left-side sleeping may make it easier for the heart to pump blood, as it doesn’t have to work against gravity.
-
Digestive System (Reducing Acid Reflux & Heartburn): This is a major benefit. The stomach sits on the left side of the body. When you sleep on your left side, the stomach and its gastric juices remain below the esophagus, helping to prevent acid from flowing back up. Sleeping on your right side has the opposite effect and can relax the lower esophageal sphincter, worsening reflux.
-
Lymphatic System: Some theories suggest the body filters toxins and waste through the lymphatic system more efficiently when sleeping on the left side, as the thoracic duct (a main lymph vessel) is on the left.
-
For Pregnant Women: This is the gold standard. Left-side sleeping improves circulation to the heart, which is beneficial for both the mother and the fetus. It also prevents the uterus from pressing on the liver, which is on the right side.
The Runner-Up: Right-Side Sleeping
While left-side is generally preferred, right-side sleeping can be better for certain people:
-
People with Heart Failure: Some studies suggest that right-side sleeping may be beneficial for those with congestive heart failure, as it may reduce heart rate and blood pressure compared to left-side sleeping. (If you have a heart condition, always consult your doctor).
-
Those Looking to Reduce Nightmares? A small study suggested that right-side sleepers reported fewer nightmares, though the reason isn’t fully understood.
The Other Positions: Back and Stomach
For context, it’s helpful to know how side-sleeping compares to other common positions:
-
Back Sleeping (Supine):
-
Pros: Excellent for spinal alignment, reduces neck and back pain, and helps prevent facial wrinkles.
-
Cons: Worsens snoring and sleep apnea because the tongue can fall back and block the airway.
-
-
Stomach Sleeping (Prone):
-
Pros: Can reduce snoring in some cases.
-
Cons: Generally considered the worst position. It puts strain on your neck and spine, often leads to back pain, and can cause facial wrinkles from pressing your face into the pillow.
-
Summary Table: Which Side is Best For You?
| If You Have This Condition… | The Recommended Side | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Acid Reflux or Heartburn | Left Side | Keeps stomach acid below the esophagus, preventing reflux. |
| Pregnancy | Left Side | Optimizes blood flow for mother and baby. |
| Snoring or Sleep Apnea | Either Side | Prevents the tongue from blocking the airway, which is a major issue when sleeping on your back. |
| Chronic Back Pain | Either Side (with a pillow between knees) | Aligns the spine and relieves pressure. |
| Heart Conditions | Consult Your Doctor | Can vary; left side is often fine, but right side may be recommended for specific issues. |
Pro Tips for All Side-Sleepers:
-
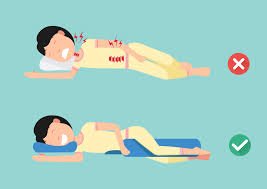
Use a Supportive Pillow: Your pillow should fill the space between your ear and shoulder to keep your neck and spine in a neutral, straight line.
-
Place a Pillow Between Your Knees: This is a game-changer! It prevents your top leg from pulling your spine out of alignment, which reduces hip and lower back strain.
-
Avoid the “Fetal Position”: Try to sleep relatively straight instead of curled up tightly, as this can restrict breathing and feel cramped in the morning.
The Bottom Line:
For the average person without specific health issues, sleeping on your left side is the most beneficial position. It promotes better digestion and heart function. However, the most important thing is to sleep in a position that is comfortable and allows you to get a restful night’s sleep.
If you have a specific health concern, especially related to your heart or breathing, it’s always best to discuss your sleep position with your doctor.